# Service 必会必知
Service 服务是 Android 四大组件之一,是 Android 提供的一种的 不需要和用户交互,且需要长期运行任务的解决方案。
Service 启动后默认是运行在主线程中,在执行具体耗时任务过程中要手动开启子线程,应用程序进程被杀死,所有依赖该进程的 Service 服务也会停止运行。
Tips
Service 是四大组件之一,同样需要在 AndroidManifest 中注册后,才能使用.
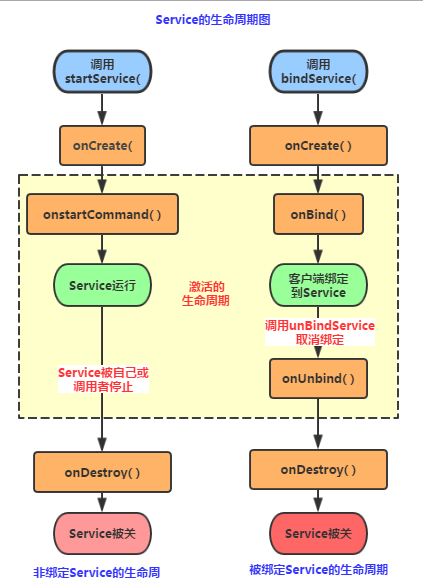
# Service 启动方式与生命周期
Service 启动方式分为两种,普通启动 startService 、绑定启动 bindService
# 普通启动 startService ()
①首次启动会创建一个 Service 实例,依次调用 onCreate () 和 onStartCommand () 方法,此时 Service 进入运行状态
②如果再次调用 StartService 启动 Service, 将不会再创建新的 Service 对象,系统会直接复用前面创建的 Service 对象,调用它的 onStartCommand () 方法!
③这样的 Service 与它的调用者无必然的联系,就是说当调用者结束了自己的生命周期,但是只要不调用 stopService, 那么 Service 还是会继续运行的!
④无论启动了多少次 Service, 只需调用一次 StopService 即可停掉 Service
- 定义 Service 服务
class TestService : Service() { | |
private val TAG = "TestService1" | |
// 必须要实现的方法 | |
override fun onBind(intent: Intent?): IBinder? { | |
Log.e(TAG, "onBind方法被调用!") | |
return null | |
} | |
//Service 被创建时调用 | |
override fun onCreate() { | |
Log.e(TAG, "onCreate方法被调用!") | |
super.onCreate() | |
} | |
//Service 被启动时调用 | |
override fun onStartCommand(intent: Intent?, flags: Int, startId: Int): Int { | |
Log.e(TAG, "onStartCommand方法被调用!") | |
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId) | |
} | |
//Service 被关闭之前回调 | |
override fun onDestroy() { | |
Log.e(TAG, "onDestory方法被调用!") | |
super.onDestroy() | |
} | |
} |
- AndroidManifest.xml 完成 Service 注册
<application> | |
<service android:name=".components.TestService1"> | |
</service> | |
</application> |
- 在 Avtivity 中 StartService 启动服务
val intent = Intent(this,TestService1::class.java); | |
startService(intent); |
- 日志输出与结果分析
TestService1: onCreate方法被调用! | |
TestService1: onStartCommand方法被调用! | |
TestService1: onStartCommand方法被调用! | |
TestService1: onStartCommand方法被调用! | |
TestService1: onStartCommand方法被调用! | |
TestService1: onDestory方法被调用! |
从上面的运行结果我们可以验证我们生命周期图中解释的内容:我们发现 onBind () 方法并没有被调用,另外多次点击启动 Service, 只会重复地调用 onStartCommand 方法!无论我们启动多少次 Service, 一个 stopService 就会停止 Service!
# 绑定启动 bindService ()
①当首次使用 bindService () 启动一个 Service 时,系统会实例化一个 Service 实例,并调用其 **onCreate () 和 onBind ()** 方法,然后调用者就可以通过返回的 IBinder 对象和 Service 进行交互了,此后如果我们再次使用 bindService 绑定 Service, 系统不会创建新的 Sevice 实例,也不会再调用 onBind () 方法,只会直接把 IBinder 对象返回给调用方
②如果我们解除与服务的绑定,只需调用 unbindService (), 此时 onUnbind 和 onDestory 方法将会被调用
③bindService 启动的 Service 服务是与调用者 (Activity) 相互关联的,可以理解为 "一条绳子上的蚂蚱", 要死一起死,在 bindService 后,一旦调用者 (Activity) 销毁,那么 Service 也立即终止
- 定义 Service 服务
class TestService2 : Service() { | |
private val TAG = "TestService2" | |
private var count = 0 | |
private var quit = false | |
// 定义 onBinder 方法所返回的对象 | |
private val binder: MyBinder = MyBinder() | |
inner class MyBinder : Binder() { | |
fun getCount(): Int { | |
return count | |
} | |
} | |
// 必须实现的方法,绑定改 Service 时回调该方法 | |
override fun onBind(intent: Intent?): IBinder { | |
Log.e(TAG, "onBind方法被调用!") | |
return binder | |
} | |
//Service 被创建时回调 | |
override fun onCreate() { | |
super.onCreate() | |
Log.e(TAG, "onCreate方法被调用!") | |
// 创建一个线程动态地修改 count 的值 | |
object : Thread() { | |
override fun run() { | |
while (!quit) { | |
try { | |
sleep(1000) | |
} catch (e: InterruptedException) { | |
e.printStackTrace() | |
} | |
count++ | |
} | |
} | |
}.start() | |
} | |
//Service 断开连接时回调 | |
override fun onUnbind(intent: Intent?): Boolean { | |
Log.i(TAG, "onUnbind方法被调用!") | |
return true | |
} | |
//Service 被关闭前回调 | |
override fun onDestroy() { | |
super.onDestroy() | |
quit = true | |
Log.i(TAG, "onDestroyed方法被调用!") | |
} | |
override fun onRebind(intent: Intent?) { | |
Log.i(TAG, "onRebind方法被调用!") | |
super.onRebind(intent) | |
} | |
} |
- AndroidManifest.xml 中注册服务
<application> | |
<service android:name=".components.TestService2"> | |
</service> | |
</application> |
- 在 Activity 中 bindService 启动服务
// 保持所启动的 Service 的 IBinder 对象,同时定义一个 ServiceConnection 对象 | |
val conn: ServiceConnection = object : ServiceConnection { | |
//Activity 与 Service 断开连接时回调该方法 | |
override fun onServiceDisconnected(name: ComponentName) { | |
println("------Service DisConnected-------") | |
} | |
//Activity 与 Service 连接成功时回调该方法 | |
override fun onServiceConnected(name: ComponentName, service: IBinder) { | |
println("------Service Connected-------") | |
binder = service as MyBinder | |
} | |
} | |
//bind 服务 | |
val intent = Intent(this,TestService::class.java) | |
bindService(intent,conn,Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) | |
start_service.setOnClickListener { | |
// 从服务获取数据 | |
Log.e("TestService2","getCount:${binder?.getCount()}") | |
} | |
// 停止按钮 | |
stop_service.setOnClickListener { | |
unbindService(conn) | |
} |
- 日志输出与结果分析
TestService2: onCreate方法被调用! | |
TestService2: onBind方法被调用! | |
TestService2: ------Service Connected------- | |
TestService2: getCount:4 | |
TestService2: getCount:6 | |
TestService2: getCount:9 | |
TestService2: onUnbind方法被调用! | |
TestService2: onDestroyed方法被调用! |
使用 BindService 绑定 Service, 依次调用 onCreate (),onBind () 方法,我们可以在 onBind () 方法中返回自定义的 IBinder 对象;再接着调用的是 ServiceConnection 的 onServiceConnected () 方法该方法中可以获得 IBinder 对象,从而进行相关操作;当 Service 解除绑定后会自动调用 onUnbind 和 onDestroyed 方法,当然绑定多客户端情况需要解除所有 的绑定才会调用 onDestoryed 方法进行销毁哦
# Android 8.0 及以上不允许后台启动 Service 服务
在一加手机上,用户升级了新版 8.0 的系统,用户将 app 切到后台,过一会儿就弹出 “xxx app 已停止运行” 的弹窗。
通过定位分析,发现下面俩前置条件
- 8.0 系统杀服务杀的很频繁
- 为了保活,我们使用了俩 Service 互保的方式
马上跑了 26 的模拟器,果然复现,日志如下:
Process: com.example.firstapp, PID: 10510 | |
java.lang.IllegalStateException: Not allowed to start service Intent { cmp=com.example.firstapp/.components.TestService }: app is in background uid UidRecord{adece9d u0a77 LAST bg:+1m35s61ms idle procs:1 seq(0,0,0)} | |
at android.app.ContextImpl.startServiceCommon(ContextImpl.java:1505) | |
at android.app.ContextImpl.startService(ContextImpl.java:1461) | |
at android.content.ContextWrapper.startService(ContextWrapper.java:644) | |
at android.content.ContextWrapper.startService(ContextWrapper.java:644) | |
at com.example.firstapp.components.TestServiceActivity$onCreate$1.run(TestServiceActivity.kt:26) |
我查阅了 android 官网,有如下一段描述:
Android 8.0 还对特定函数做出了以下变更:
- 如果针对 Android 8.0 的应用尝试在不允许其创建后台服务的情况下使用
startService()函数,则该函数将引发一个IllegalStateException。- 新的
Context.startForegroundService()函数将启动一个前台服务。现在,即使应用在后台运行,系统也允许其调用Context.startForegroundService()。不过,应用必须在创建服务后的五秒内调用该服务的startForeground()函数。
解决方法就很简单了,把 Service 互启的逻辑块改为:
- AndroidManifest.xml 声明权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE" /> |
- 服务启动兼容写法
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 26) { | |
context.startForegroundService(intent); | |
} else { | |
// Pre-O behavior. | |
context.startService(intent); | |
} | |
class TestService:Service(){ | |
// 发送一个前台通知 | |
override fun onCreate(){ | |
val notification: Notification =Notification.Builder(applicationContext, "channel_id").build() | |
startForeground( 1, notification) | |
} | |
} |
在被启动的 Service 创建服务后的五秒内调用 startForground(0, new Notification()) ,如果不调用或调用时间超过 5 秒会抛出一个 ANR。