# 背景
随着 vue3 的逐渐成熟,公司项目逐渐会存在 vue2 和 vue3 项目共存的情况,兼容 vue2 和 vue3 的公共组件开发能让老项目较好地过渡到 vue3。研究了 vue-demi 的源码和 demo,发现 vue-demi 只是简单地根据 vue 版本生成对应的类似中间件的东西,而且 render 函数也只是做了简单的中转处理;
国外大佬写了一个 vue-demi 解决了 vue2/vue3 的 render 函数 attrs 属性的问题,这里我就直接贴 issue 链接,不做过多说明了: github.com/vueuse/vue-…
虽然 vue-demi 没有提供 sfc 的兼容方案,但是其实仔细想一下,sfc 的解析处理也不应该是由 vue-demi 来解决,应该是交给打包工具将 template 转成 render,而 vue-demi 只需要关注 composition-api 就行;于是往着这个思路,花了几天时间研究一下 vue2.6、vue2.7 和 vue3 的 sfc-compiler,得到以下开发方案。
# 技术要点
# vue-demi
查看源码可以发现,vue-demi 的工作是通过 postinstall 和 npx vue-demi-fix 指令,判断当前项目安装的 vue 版本,然后将对应版本的插件复制到 lib 的根目录,其插件的功能就是抹平 vue2 和 vue3 版本使用 composition-api 时的差异;
<=2.6: exports from vue + @vue/composition-api with plugin auto installing. | |
2.7: exports from vue (Composition API is built-in in Vue 2.7). | |
>=3.0: exports from vue, with polyfill of Vue 2's set and del API. |
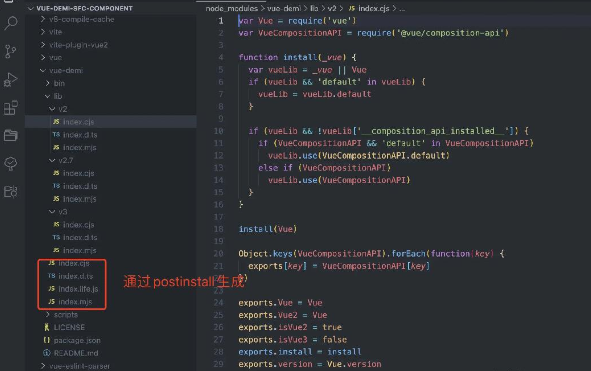
# sfc compiler
在日常开发中写的 vue template,实际上最后是通过 sfc-compiler 转成 render 函数输出的,而 vue2 和 vue3 的 sfc-compiler 是互不兼容的。尤大大已经提供了 vue2.6.x,vue2.7 和 vue3 的 compiler,其实我们只需要在打包工具写判断不同的 vue 版本使用不同的 compiler 逻辑即可,本文是基于 vite 开发,以下对应的打包插件:
vue2.6: vite-plugin-vue2@2.6.14 + vue-template-compiler@2.6.14 | |
vue2.7: vite-plugin-vue2@2.7.9 + vue-template-compiler@2.7.9; 或者@vitejs/plugin-vue2 + @vue/compiler-sfc | |
vue3: @vitejs/plugin-vue + @vue/compiler-sfc |
# 实现方式
以下实现方式均是基于 vite 开发,换成 webpack 和 rollup 原理上也是替换对应的插件即可。
# vue2.6 + vue3 + vite + vue-demi
以 vue2.6 为主包,开发 vue2/vue3 组件,该方式能做到通过一个 package.json 的 scripts 同时调试和打包 vue2、vue3 环境,以下讲一下重点;
# package.json
package.json 中的 vue 包是固定了 2.6.14 版本,这里要注意 vue-template-compiler 要和 vue 的版本对齐;
scripts 中的 switch:2 指令没有按照文档说的使用 npx vue-demi-switch,是因为在实际调试过程中,由于 vite 是会缓存依赖的,dev 调试时 vue-demi-switch 会出现一些莫名其妙的问题,具体原因我还没搞明白,所以就改成用 npx vue-demi-fix。
//package.json 部分片段 | |
"main": "./lib/vue-demi-sfc-component.umd.cjs", | |
"exports": { | |
".": { | |
"import": "./lib/vue-demi-sfc-component.js", | |
"require": "./lib/vue-demi-sfc-component.umd.cjs" | |
} | |
}, | |
"scripts": { | |
"postinstall": "node ./scripts/postinstall.mjs", | |
"dev": "vite", | |
"dev:3": "npm run switch:3 && vite --force", | |
"dev:2": "npm run switch:2 && vite", | |
"switch:2": "npx vue-demi-fix", | |
"switch:3": "npx vue-demi-switch 3 vue3", | |
"build:3": "npm run switch:3 && vue-tsc --noEmit && vite build", | |
"build:2": "npm run switch:2 && vue-tsc --noEmit && vite build", | |
"build": "rimraf lib && npm run build:2 && npm run build:3", | |
"preview": "vite preview", | |
"lint:fix": "eslint . --ext .js,.ts,.vue --fix", | |
"prepare": "husky install", | |
"pub": "npm publish --access=public" | |
}, | |
"dependencies": { | |
"@vue/composition-api": "^1.7.0", | |
"vue-demi": "^0.13.8" | |
}, | |
"peerDependencies": { | |
"@vue/composition-api": "^1.7.0", | |
"vue": "^2.0.0 || >=3.0.0" | |
}, | |
"peerDependenciesMeta": { | |
"@vue/composition-api": { | |
"optional": true | |
} | |
}, | |
"peerDependencies": { | |
"@vue/composition-api": "^1.7.0", | |
"vue": "^2.0.0 || >=3.0.0" | |
}, | |
"peerDependenciesMeta": { | |
"@vue/composition-api": { | |
"optional": true | |
} | |
}, | |
"devDependencies": { | |
//... 其他依赖,这里就不复制了 | |
"@vitejs/plugin-vue": "^3.0.3", | |
"vite": "^3.0.7", | |
"vite-plugin-vue2": "^2.0.2", | |
"vue": "2.6.14", | |
"vue-eslint-parser": "^9.0.3", | |
"vue-template-compiler": "2.6.14", | |
"vue-tsc": "^0.39.5", | |
"vue2": "npm:vue@2.6.14", | |
"vue3": "npm:vue@^3.2.36" | |
} |
# vite.config.ts
import { defineConfig } from 'vite' | |
import { createVuePlugin } from 'vite-plugin-vue2' | |
import * as compiler from '@vue/compiler-sfc' | |
import vue3 from '@vitejs/plugin-vue' | |
import path from 'path' | |
import { getLibDir } from './scripts/utils.mjs' | |
import { isVue2, version } from 'vue-demi' | |
console.log({ version }) | |
const resolve = (str: string) => { | |
return path.resolve(__dirname, str) | |
} | |
// https://vitejs.dev/config/ | |
export default defineConfig({ | |
resolve: { | |
alias: { | |
'@': resolve('src'), | |
vue: isVue2 ? resolve('/node_modules/vue2') : resolve('/node_modules/vue3') | |
} | |
}, | |
build: { | |
lib: { | |
entry: resolve('./src/components/index.ts'), | |
name: 'vueDemiSfcComponent', | |
fileName: 'vue-demi-sfc-component' | |
}, | |
cssTarget: 'chrome61', | |
rollupOptions: { | |
external: ['vue-demi', 'vue'], | |
output: { | |
dir: getLibDir(version), | |
globals: { | |
vue: 'Vue', | |
'vue-demi': 'VueDemi' | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
}, | |
optimizeDeps: { | |
exclude: ['vue-demi'] | |
}, | |
plugins: [ | |
isVue2 | |
? createVuePlugin() | |
: vue3({ | |
compiler: compiler | |
}) | |
] | |
}) |
1. 这个文件有几个关键逻辑:
import { isVue2, version } from 'vue-demi' |
2、alias 要根据环境切换地址
alias: { | |
'@': resolve('src'), | |
vue: isVue2 ? resolve('/node_modules/vue2') : resolve('/node_modules/vue3') | |
} |
3、在以 vue2.6 为主包的时候,如果直接使用 @vitejs/plugin-vue, 打包时会报错
error when starting dev server: | |
Error: Failed to resolve vue/compiler-sfc. | |
@vitejs/plugin-vue requires vue (>=3.2.25) to be present in the dependency tree. |
这是因为 @vitejs/plugin-vue 源码中是直接找 vue/compiler-sfc 目录的,如果以 vue2 为主包,这个时候 nod_modules/vue 是 vue2 的目录结构,并没有 vue/compiler-sfc ;
function resolveCompiler(root) { | |
const compiler = tryRequire("vue/compiler-sfc", root) || tryRequire("vue/compiler-sfc"); | |
if (!compiler) { | |
throw new Error( | |
`Failed to resolve vue/compiler-sfc. | |
@vitejs/plugin-vue requires vue (>=3.2.25) to be present in the dependency tree.` | |
); | |
} | |
return compiler; | |
} |
所以就去寻找一下 @vitejs/plugin-vue 的 options
interface Options { | |
include?: string | RegExp | (string | RegExp)[]; | |
exclude?: string | RegExp | (string | RegExp)[]; | |
isProduction?: boolean; | |
script?: Partial<Pick<SFCScriptCompileOptions, 'babelParserPlugins'>>; | |
template?: Partial<Pick<SFCTemplateCompileOptions, 'compiler' | 'compilerOptions' | 'preprocessOptions' | 'preprocessCustomRequire' | 'transformAssetUrls'>>; | |
style?: Partial<Pick<SFCStyleCompileOptions, 'trim'>>; | |
/** | |
* Transform Vue SFCs into custom elements. | |
* - `true`: all `*.vue` imports are converted into custom elements | |
* - `string | RegExp`: matched files are converted into custom elements | |
* | |
* @default /\.ce\.vue$/ | |
*/ | |
customElement?: boolean | string | RegExp | (string | RegExp)[]; | |
/** | |
* Enable Vue reactivity transform (experimental). | |
* https://github.com/vuejs/core/tree/master/packages/reactivity-transform | |
* - `true`: transform will be enabled for all vue,js(x),ts(x) files except | |
* those inside node_modules | |
* - `string | RegExp`: apply to vue + only matched files (will include | |
* node_modules, so specify directories in necessary) | |
* - `false`: disable in all cases | |
* | |
* @default false | |
*/ | |
reactivityTransform?: boolean | string | RegExp | (string | RegExp)[]; | |
/** | |
* Use custom compiler-sfc instance. Can be used to force a specific version. | |
*/ | |
compiler?: typeof _compiler; | |
} |
发现 option 中是有自定义 compiler-sfc 的参数,于是就得到以下方案:
// vite.config.ts | |
import * as compiler from '@vue/compiler-sfc' | |
export default defineConfig({ | |
// ... | |
plugins: [ | |
isVue2 | |
? createVuePlugin() | |
: vue3({ | |
compiler: compiler | |
}) | |
] | |
}) |
# main.ts
main.ts 需要判断 isVue2 后,区分 vue2 和 vue3 的依赖
import { isVue2 } from 'vue-demi' | |
import { createApp } from 'vue3' | |
import Vue2 from 'vue2' | |
import './style.css' | |
import App from './App.vue' | |
if (isVue2) { | |
const app = new Vue2({ | |
render: (h) => h(App) | |
}) | |
app.$mount('#app') | |
} else { | |
const app = createApp(App) | |
app.mount('#app') | |
} |
# postinstall
这里是模仿 vue-demi 的原理,在安装时利用 postinstall 钩子执行 node 脚本,复制 lib 中的 v2/v3 目录,具体可直接看文章最后的项目链接;这里有一个地方要注意,由于我是使用 vite + ts 构建的项目,package.json 中的 "type": "module" 需要我把所有 js 改成 mjs 文件,这个时候,其他项目安装这个项目时,会找不到 __dirname,因此 utils.mjs 加了以下逻辑。
import { fileURLToPath } from 'url' | |
const __filename = fileURLToPath(import.meta.url) | |
const __dirname = path.dirname(__filename) |
# vue2.7 + vue3 + vite + vue-demi + yarn workspaces
以 vue2.7 为主包开发时,没办法像 vue2.6 可以在一个 package.json 项目下调试和打包,主要是因为 vue2.7 的代码方式已经是 monorepo 项目,因此在安装 vue2.7 的时候,会重新下载 @vue/compuler-sfc 的 2.7.x 版本。

所以没办法直接使用 @vue/compiler-sfc 包作为 vue3 的 compiler;
那么我们就要换一个思路,做 node_modules 隔离,而 node_modules 隔离的方案现在主流的就是 yarn workspaces、lerna 和 pnpm,这里我就以 yarn workspaces 来简单讲一下思路;
(ps: 该方式我并没有上传到 github)
开启 yarn workspaces 之后,新建 packages 文件夹
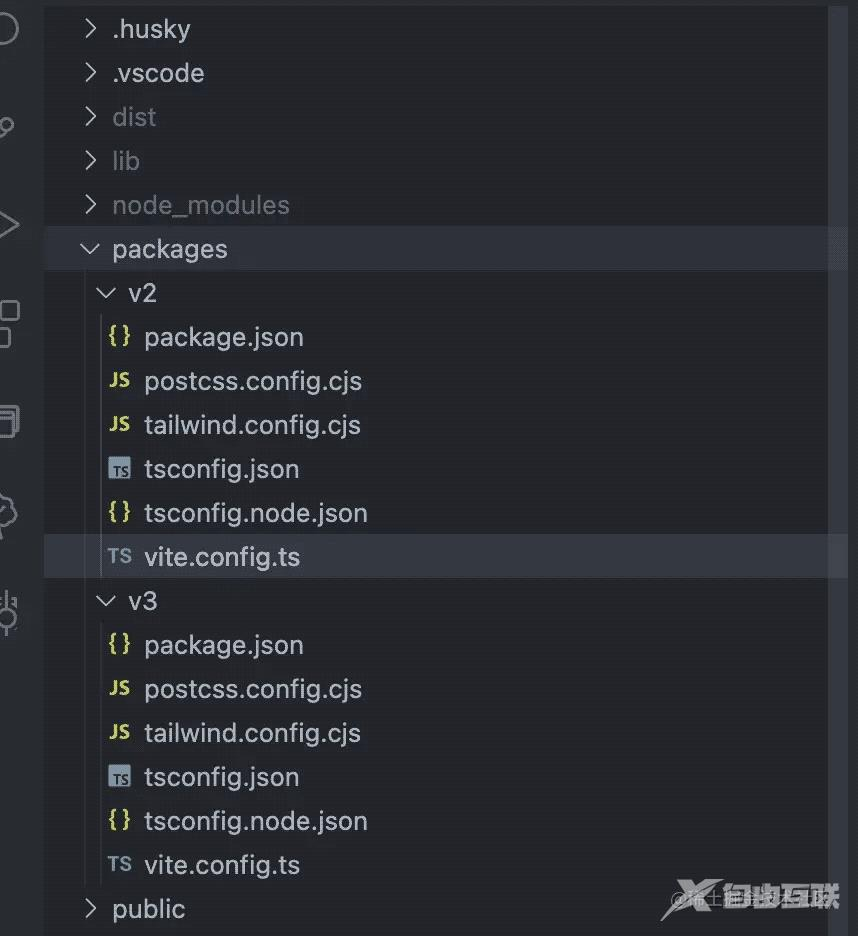
然后再 packages 下分别新建 v2 和 v3 目录,这两个目录存放对应 vue2 和 vue3 的 package.json 和 vite.config.ts
// v2/package.json | |
"scripts": { | |
"dev": "vite", | |
"build": "rimraf lib/v2 && vue-tsc --noEmit && vite build", | |
"preview": "vite preview", | |
"lint:fix": "eslint . --ext .js,.ts,.vue --fix", | |
"prepare": "husky install", | |
"pub": "npm publish --access=public" | |
}, | |
"devDependencies": { | |
"@vitejs/plugin-vue2": "^2.7.9", | |
"vite": "^3.0.7", | |
"vite-plugin-vue2": "^2.0.2", | |
"vue": "2.7.9", | |
"vue-eslint-parser": "^9.0.3", | |
"vue-template-compiler": "2.7.9", | |
"vue-tsc": "^0.39.5", | |
"vue2": "npm:vue@2.7.9", | |
"vue3": "npm:vue@^3.2.36" | |
} | |
// v3/package.json | |
"scripts": { | |
"dev": "vite", | |
"build": "rimraf lib/v3 && vue-tsc --noEmit && vite build", | |
"preview": "vite preview", | |
"lint:fix": "eslint . --ext .js,.ts,.vue --fix", | |
"prepare": "husky install", | |
"pub": "npm publish --access=public" | |
}, | |
"devDependencies": { | |
"@vitejs/plugin-vue": "^3.0.3", | |
"vite": "^3.0.7", | |
"vite-plugin-vue2": "^2.0.2", | |
"vue": "3.2.26", | |
"vue-eslint-parser": "^9.0.3", | |
"vue-template-compiler": "2.6.14", | |
"vue-tsc": "^0.39.5", | |
"vue2": "npm:vue@2.6.14", | |
"vue3": "npm:vue@^3.2.26" | |
} |
vite.config.ts 的区别主要是 rollupOptions.output.dir,和对应的 plugin,然后 alias 不需要再指定 vue 路径,main.ts 也不需要区分 vue2 和 vue3 的依赖;
// v2/vite.config.ts | |
import { defineConfig } from 'vite' | |
import { createVuePlugin } from 'vite-plugin-vue2' | |
// or import vue2 from '@vitejs/plugin-vue2' | |
import path from 'path' | |
const resolve = (str: string) => { | |
return path.resolve(__dirname, str) | |
} | |
// https://vitejs.dev/config/ | |
export default defineConfig({ | |
// ... | |
resolve: { | |
alias: { | |
'@': resolve('src'), | |
} | |
}, | |
build: { | |
// ... | |
rollupOptions: { | |
external: ['vue-demi', 'vue'], | |
output: { | |
dir: resolve('../../lib/v2'), // 区别在这 | |
globals: { | |
vue: 'Vue', | |
'vue-demi': 'VueDemi' | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
}, | |
optimizeDeps: { | |
exclude: ['vue-demi'] | |
}, | |
plugins: [createVuePlugin()] // or vue2() | |
}) | |
// v3/vite.config.ts | |
import { defineConfig } from 'vite' | |
import vue3 from '@vitejs/plugin-vue' | |
import path from 'path' | |
const resolve = (str: string) => { | |
return path.resolve(__dirname, str) | |
} | |
// https://vitejs.dev/config/ | |
export default defineConfig({ | |
// ... | |
resolve: { | |
alias: { | |
'@': resolve('src'), | |
} | |
}, | |
build: { | |
rollupOptions: { | |
external: ['vue-demi', 'vue'], | |
output: { | |
dir: resolve('../../lib/v3'), // 区别在这 | |
globals: { | |
vue: 'Vue', | |
'vue-demi': 'VueDemi' | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
}, | |
optimizeDeps: { | |
exclude: ['vue-demi'] | |
}, | |
plugins: [vue3()] | |
}) |
main.ts
// main.ts | |
import { createApp } from 'vue-demi' | |
import './style.css' | |
const app = createApp(App) | |
app.mount('#app') |
整体目录结构如下,最后通过 node 脚本去同时构建 v2 和 v3 即可。

# 目前没找到 vue3 为主包的开发方式
文章看到这里,大概能知道整个方案其实是基于 vue-demi 处理 composition-api 和使用 vue3 的自定义 compiler 处理分别打包 vue2、vue3;而 vite-plugin-vue2 是没有对应自定义 compiler 的 options,并且在 vue3 为主包的情况下,会报 vue-template-compiler 与 vue 版本不一致的错误;而 @vitejs/plugin-vue2 存在跟 vue3 冲突的情况;
目前如果要基于 vue3 为主包的方式开发,我想到如下 2 个思路,待后续有时间再去验证:
vite-plugin-vue2 增加自定义 compiler 选项
开发 rollup 插件,支持修改 vue-template-compiler 在读取 require (vue) 时,重定向到 "vue2": "npm:vue@2.6.14" 对应的路径
# 注意点
1、@vue/composition-api 重复引用问题
由于 vue-demi 在 v2.6 的场景下,会自动 install @vue/composition-api,,如果项目自身也在需要在入口时注册 @vue/composition-api,会出现多次注册 @vue/composition-api 实例的情况,导致出 setup 相关的报错,这时需要在项目的 alias 加上以下代码:
alias: { | |
'@vue/compostion-api': resolve('./node_modules/@vue/composition-api') | |
}, |
2、由于要兼容 vue2,vue3 的 setup sfc 语法糖不兼容
这一点无法解决,写组件 template 的时候,还是只能用 vue2 的 template 写法,包括 template 还是需要有唯一的跟节点;
最后
写到最后,其实我发现去写兼容 vue2 和 vue3 的 template 代码,并不能完全解决 vue2 到 vue3 过渡的问题。希望 vue3 社区以后越来越完善~
贴上项目地址 (vue2.6 + vue3 + vite + vue-demi):vue-demi-sfc-component
https://github.com/sakibcc/vue-demi-sfc-component
以上就是 vue demi 支持 sfc 方式的 vue2vue3 通用库开发详解的详细内容